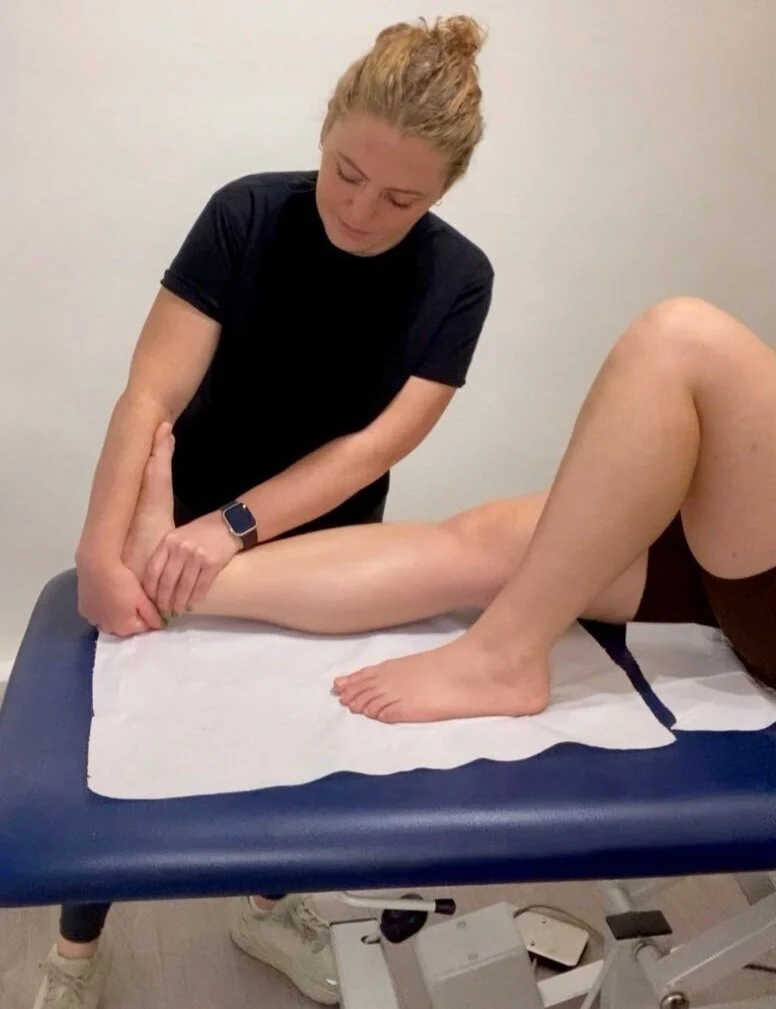
How Osteopathy Can Aid in Sports Injury Treatment
Sports injuries are an unfortunate reality for many athletes as well as active individuals. Whether it's a sprained ankle, a strained muscle, or a more serious injury like a torn ligament, these setbacks can hinder performance and quality of life. Advise and research around a sports injury treatment is constantly changing. While in the past it was believed rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) was advised this has now changed. For acute soft tissue injuries it is now recommended to use the acronym PEACE and LOVE. In this blog we will go into the latest recommendation for optimal post injury recovery and how osteopathy can aid in sports injury treatment.
Soft tissue and sports injury treatment: PEACE and LOVE method
During the first few days after an injury in is recommended to use PEACE:
Protect: You want to reduce the load and movement being put through the joint or tissue injured to reduce the risk of aggravating the injury. However, it is important to not completely stop moving it, as prolonged periods of immobility can have a negative impact on the tissue’s strength and quality. At this stage it is recommended to keep gently moving without loading the injured area.
Elevate: This helps promote fluid drainage out of the injured area.
Avoid anti-inflammatories: In the early stage of the injury the inflammatory process helps with the healing process. Taking anti-inflammatory may have a negative effect on the long-term healing process of the sports injury. For this reason it is also now recommended to avoid ice at this stage as it may disrupt the inflammation and other tissue healing processes.
Compress: this can help with tissue haemorrhage and intra-articular oedema
Educate: Education is key! Understanding what is happening to the body and the tissue during the healing process is crucial. It will allow the injured individual to take a more active approach in the recovery and have realistic expectations.
The next stage of recovery for a soft tissue sports injury recovery is LOVE:
Load: It is crucial for optimal recovery to take an active approach which involves both mobility work and exercises. Return to normal activities should be initiated as soon as the symptoms allow it. By returning to activity while staying pain free promotes the repair and strengthening of the tissue in question.
Optimism: big part of the rehabilitation process comes from the metal state of the injured individual. Try to avoid catastrophizing or being fearful and try to stay realistic and optimist! It will improve your chances of optimal recovery.
Vascularisation: Musculoskeletal injury, such as sports injuries, management needs to include cardiovascular exercises as it can increase blood flow to the injured area.
Exercise: Excercise based rehabilitation is crucial for optimal recovery. It can help with restoring mobility, strength and proprioception. It is important to use pain as a guide and to gradually progress with the exercises.
The Role of Osteopathy in Sports Injury Treatment:
When it comes to sports injuries, osteopathy offers a unique approach that goes beyond simply treating the symptoms. Here are several ways in which osteopathy can aid in sports injury treatment:
Manual Therapy: Osteopathic treatments often involve hands-on techniques such as soft tissue massage, joint mobilization, and stretching exercises. These techniques help improve range of motion, reduce muscle tension, and promote tissue healing. For individuals recovering from injuries like sprains or strains, manual therapy can accelerate the healing process and restore function.
Assessment of the body’s biomechanics: Osteopaths are trained to assess posture and body mechanics. They can identifying any areas which be contributing to sports injuries or compensating for the sports injury. By correcting these issues through targeted exercises and adjustments, osteopathic treatment can help prevent future injuries and improve overall performance.
Pain Management: Sports injuries can be accompanied by significant pain, which can impact an athlete's ability to train and compete. Osteopathic techniques aim to alleviate pain through gentle manipulation of the affected areas, reducing reliance on pain medications and promoting natural pain relief mechanisms within the body.
Enhanced Healing: Osteopathy focuses on improving blood flow and lymphatic drainage, which are essential for the body's healing processes. By enhancing circulation to injured tissues, osteopathic treatments can accelerate healing and reduce recovery time.
Individualized Treatment Plans: One of the hallmarks of osteopathy is its personalized approach to treatment. Osteopaths take into account the athlete's unique anatomy, injury history, and specific goals to create a tailored treatment plan. This comprehensive approach addresses not only the current injury but also underlying factors that may contribute to recurrent injuries.
Sports injuries can be very stressful and debilitating and it may be overwhelming and hard to understand what to do and where to start from. Sports injury treatment and management are continuously evolving; it is crucial to adhere to the latest evidence to maximise your chances of achieving a complete recovery. By properly adhering to the rehab plan and getting appropriate individualised advice from a qualified healthcare professional such as an osteopath or physiotherapist, preventative measures can be put in place to reduce the risk for future sports injuries.
We hope this information is useful for you. If you need advice or have any questions about osteopathy, please contact us. You can find us just a few minutes walk from Clapham Common station. We are always happy to help. If you like this blog, please share!
References:
Dubois, B. and Esculier, J.-F. (2019). Soft-tissue Injuries Simply Need PEACE and LOVE. British Journal of Sports Medicine, 54(2), p.bjsports-2019-101253. doi:https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsports-2019-101253.
Short, S., Tuttle, M. and Youngman, D. (2023). A Clinically-Reasoned Approach to Manual Therapy in Sports Physical Therapy. International Journal of Sports Physical Therapy, 18(1). doi:https://doi.org/10.26603/001c.67936.